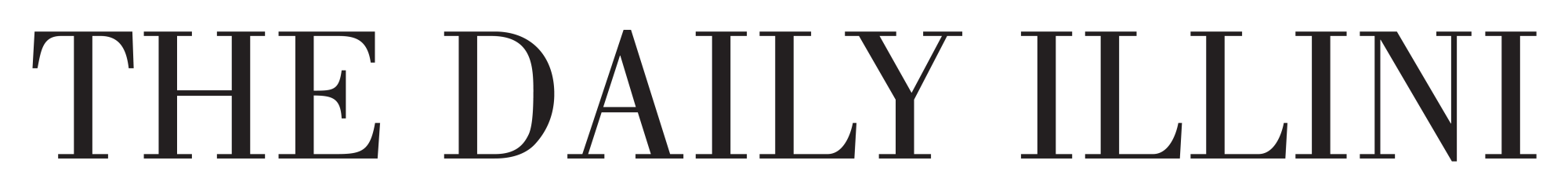Space shuttle takes off well, without issue
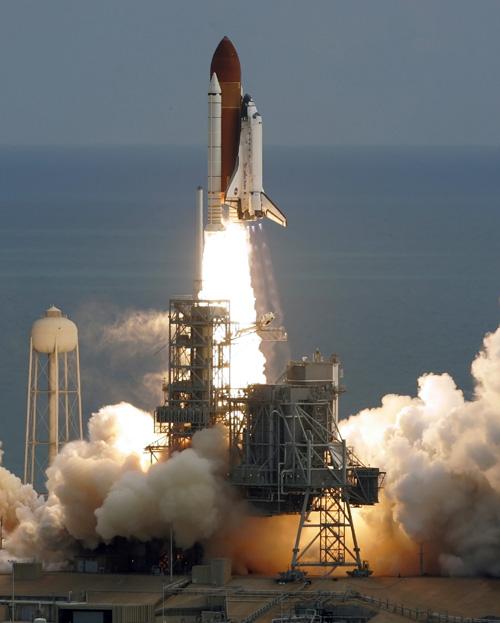
The space shuttle Discovery lifts off Tuesday at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Erica Magda
Oct 24, 2007
Last updated on May 12, 2016 at 05:44 p.m.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Shuttle Discovery and its crew of seven thundered into orbit Tuesday, setting off on the most challenging space station construction mission yet that will pave the way for the arrival of two science labs in a few months.
NASA pulled off the on-time launch – the third one in a row – after determining that a small patch of ice on fuel tank plumbing posed no danger. Indeed, most if not all of the ice harmlessly shook loose when the booster rockets and engines ignited.
The rain clouds that had been forecast for days stayed away for the late morning launch.
“We got lucky today. We could have just as easily gotten unlucky,” said launch director Mike Leinbach. “But as I tell my team, there’s nothing wrong every now and then with a little good luck.”
Get The Daily Illini in your inbox!
With Discovery safely in orbit, NASA looked ahead to all the work awaiting the astronauts once they arrive at the international space station on Thursday. It is considered the most complicated mission in the nine years of station assembly in orbit.
During their 1«-week station visit, the astronauts must install a live-in compartment that they’re bringing along, relocate a giant girder and set of solar wings, extend those solar wings and radiators, and test a thermal tile repair kit.
In all, five spacewalks are planned, which will be the most ever conducted while a shuttle is docked at the station.
The three space station residents face even more construction chores after the shuttle leaves, each one of them critical. NASA’s space operations chief, Bill Gerstenmaier, said the two crews face a tremendous series of challenges but noted, “I can’t think of a better start to this mission than what we got today.”
In a historic coincidence, both the shuttle and station have women at the helm. Retired Air Force Col. Pamela Melroy is only the second woman to command a shuttle, and biochemist Peggy Whitson is the first female skipper of a space station.
Whitson and Clay Anderson watched Discovery’s launch live on a station computer. Anderson, who will return to Earth aboard Discovery after a five-month expedition, shook a white towel and did a complete backflip once the shuttle reached orbit.
At least six pieces of foam insulation came off Discovery’s fuel tank during liftoff, but because that occurred after the crucial first two minutes, the debris posed no risk to the shuttle.
“It’s preliminary only, but it did look like a clean ascent,” Mission Control informed Melroy.
A much smaller piece of foam broke off a bracket on the fuel tank during the last launch in August, possibly along with some ice, and gouged Endeavour’s belly. More changes were made to Discovery’s fuel tank to prevent dangerous ice buildup from the super-cold propellants.
Melroy and her crew will use a laser-tipped inspection boom Wednesday to check Discovery’s vulnerable wings and nose, standard procedure since the 2003 Columbia accident.
They’ll pay particular attention to three of the 44 panels on the leading edges of Discovery’s wings that may have cracks just beneath a protective coating. Even though NASA’s own safety group wanted to delay the launch, senior managers decided a week ago that wing repairs were unnecessary.
Discovery’s primary payload is the Italian-built compartment, about the size of a small bus. An Italian astronaut making his first spaceflight, Paolo Nespoli, is personally delivering the chamber, named Harmony by schoolchildren who took part in a national competition. About 130 of those youngsters were on hand for the launch.
Europe and Japan’s laboratories will hook up to Harmony. The European lab, named Columbus, is targeted for a Dec. 6 launch. The Japanese lab will follow in two segments in February and April.
NASA is up against a hard 2010 deadline for completing the space station and retiring the three remaining shuttles.