Italian mobster memberships declining in many major cities

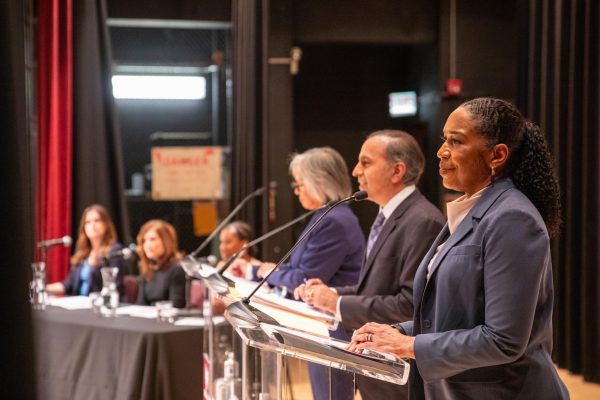
Reputed Mafia kingpin Vincent “The Chin” Gigante, center, is swarmed by photographers as he gets into a car in New York enroute to his trial in federal court, in this file photo from June 27, 1997. Mob membership in key cities is falling. Erica Magda
Oct 26, 2007
Last updated on May 12, 2016 at 05:52 p.m.
NEW YORK – In early 2004, mob veteran Vincent Basciano took over as head of the Bonanno crime family. The reign of the preening, pompadoured Mafioso known as Vinny Gorgeous lasted only slightly longer than a coloring dye job from his Bronx hair salon.
Within a year, the ex-beauty shop owner with the hair-trigger temper was behind bars – betrayed by his predecessor, a stand-up guy now sitting down with the FBI.
It was a huge blow to Basciano and the once-mighty Bonannos, and similar scenarios are playing out from coast to coast. The Mafia, memorably described as “bigger than U.S. Steel” by mob financier Meyer Lansky, is more of an illicit mom-and-pop operation in the new millennium.
The mob’s frailties were evident in recent months in Chicago, where three senior-citizen mobsters were locked up for murders committed a generation ago; in Florida, where a 97-year-old Mafioso with a rap sheet dating to the days of Lucky Luciano was imprisoned for racketeering; and in New York, where 80-something boss Matty “The Horse” Ianniello pleaded to charges linked to the garbage industry and union corruption.
Get The Daily Illini in your inbox!
Things are so bad that mob scion John A. “Junior” Gotti chose to quit the mob while serving five years in prison rather than return to his spot atop the Gambino family.
At the mob’s peak in the late 1950s, more than two dozen families operated nationwide. Disputes were settled by the Commission, a sort of gangland Supreme Court. Corporate change came in a spray of gunfire. This was the mob of “The Godfather” celebrated in pop culture.
Today, Mafia families in former strongholds like Cleveland, Los Angeles and Tampa are gone. La Cosa Nostra – our thing, as its initiates called the mob – is in serious decline everywhere but New York City. And even there, things aren’t so great: Two of New York’s five crime families are run in absentia by bosses behind bars.
Mob executions are also a blast from the past. The last boss whacked was the Gambinos’ “Big Paul” Castellano in 1985. New York’s last mob shooting war occurred in 1991. And in Chicago, home to the 1929 St. Valentine’s Day massacre, the last hit linked to the “Outfit” went down in the mid-1990s.
The Mafia’s ruling Commission has not met in years. Membership in key cities is dwindling, while the number of mob turncoats is soaring.
“You arrest 10 people,” says one New York FBI agent, “and you have eight of them almost immediately knocking on your door: ‘OK, I wanna cut a deal.'”
The oath of omerta – silence – has become a joke. “Family” values that served as cornerstones for an organization brought to America by Italian immigrants during the era of Prohibition.
Associated Press writers Curt Anderson, Denise Lavoie, Jeremiah Marquez, Dave Porter and Maryclaire Dale contributed to this report